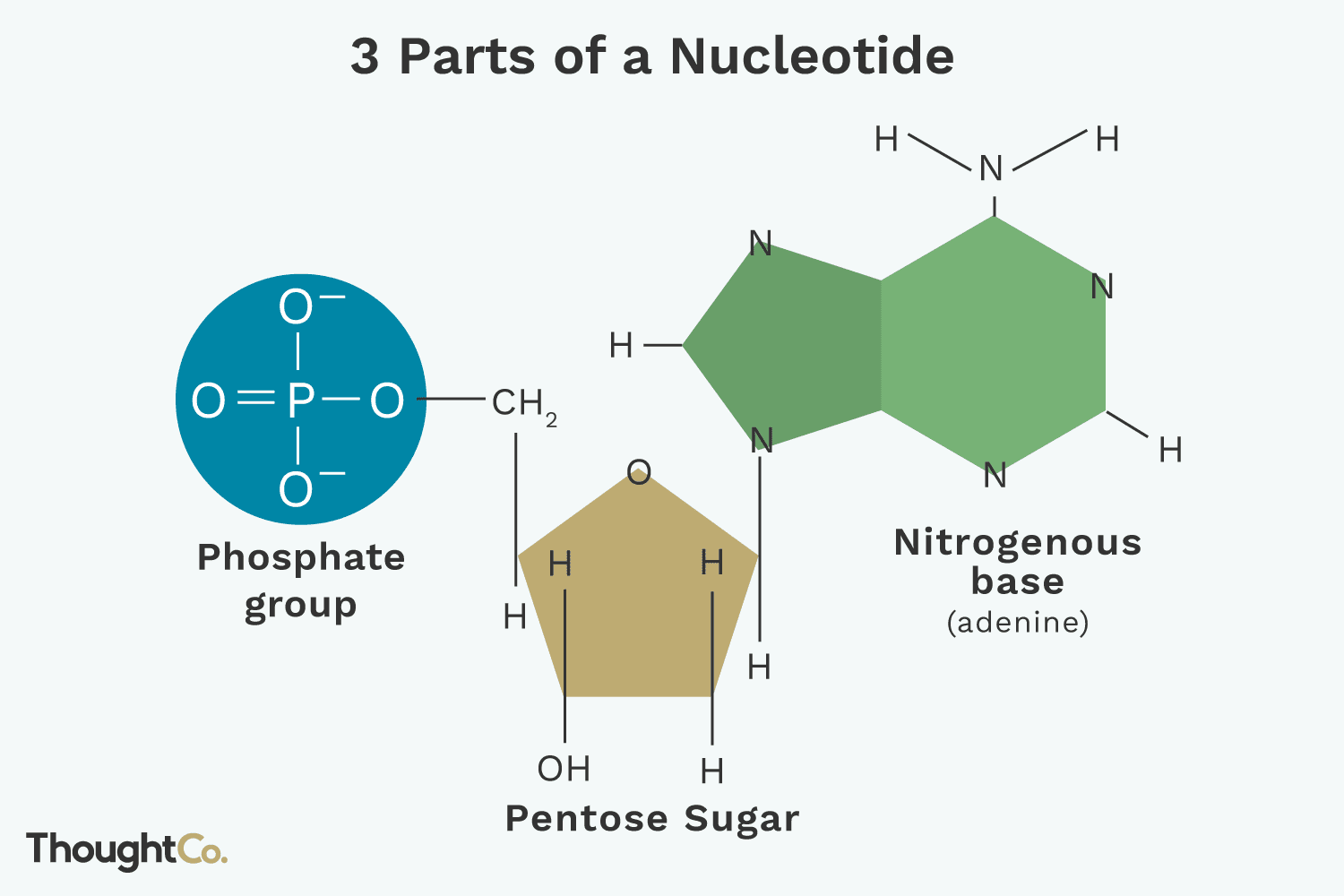
Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, which are essential molecules for life. Each nucleotide consists of three fundamental components that work together to store genetic information and facilitate a variety of cellular processes. These three components are:
- A Nitrogenous Base
The nitrogenous base is a crucial part of the nucleotide, responsible for pairing with other bases to form the double-stranded structure of DNA or single strands in RNA. There are two types of nitrogenous bases:
- Purines: Adenine (A) and Guanine (G), which are double-ringed structures.
- Pyrimidines: Cytosine (C), Thymine (T) in DNA, and Uracil (U) in RNA, which are single-ringed structures.
- A Five-Carbon Sugar (Pentose Sugar)
The five-carbon sugar provides the backbone for nucleotides and connects the nitrogenous base to the phosphate group. The type of sugar determines whether the nucleotide is part of DNA or RNA:
- Deoxyribose is the sugar in DNA, which lacks one oxygen atom compared to ribose.
- Ribose is the sugar in RNA, which contains a hydroxyl group (-OH) at the 2' carbon position.
- A Phosphate Group The phosphate group links nucleotides together to form long chains, such as DNA and RNA strands. Each nucleotide can contain one to three phosphate groups, but in nucleic acids, only one phosphate group is attached. The phosphate group connects the 5' carbon of one nucleotide's sugar to the 3' carbon of another nucleotide’s sugar, creating a sugar-phosphate backbone.This phosphate-sugar linkage is vital for the structural integrity of DNA and RNA. The negatively charged phosphate groups also contribute to the overall negative charge of DNA, which plays a role in the molecule's interactions with proteins and other molecules within the cell.
Summary
The three key components of a nucleotide—the nitrogenous base, the five-carbon sugar, and the phosphate group—each play a specific role in forming the structure and function of DNA and RNA. The combination of these components enables the storage and transmission of genetic information, essential for cellular functions and the continuity of life.Read more :
1= https://bulkdrchecker.com/blogs/what-are-the-worst-side-effects-of-losartan/
2= https://bulkdrchecker.com/blogs/what-are-the-three-credit-reporting-agencies/
3= https://bulkdrchecker.com/blogs/what-are-the-three-components-of-a-nucleotide/
4= https://bulkdrchecker.com/blogs/what-are-the-the-seven-continents/
5= https://bulkdrchecker.com/blogs/what-are-the-primary-colors/