Mars, often referred to as the "Red Planet," is a cold and arid world. Due to its distance from the Sun and thin atmosphere, Temperatures on Mars vary greatly and are generally much colder than those on Earth. Understanding these temperature extremes is critical for future exploration and potential human settlement on the planet.
Average Temperature
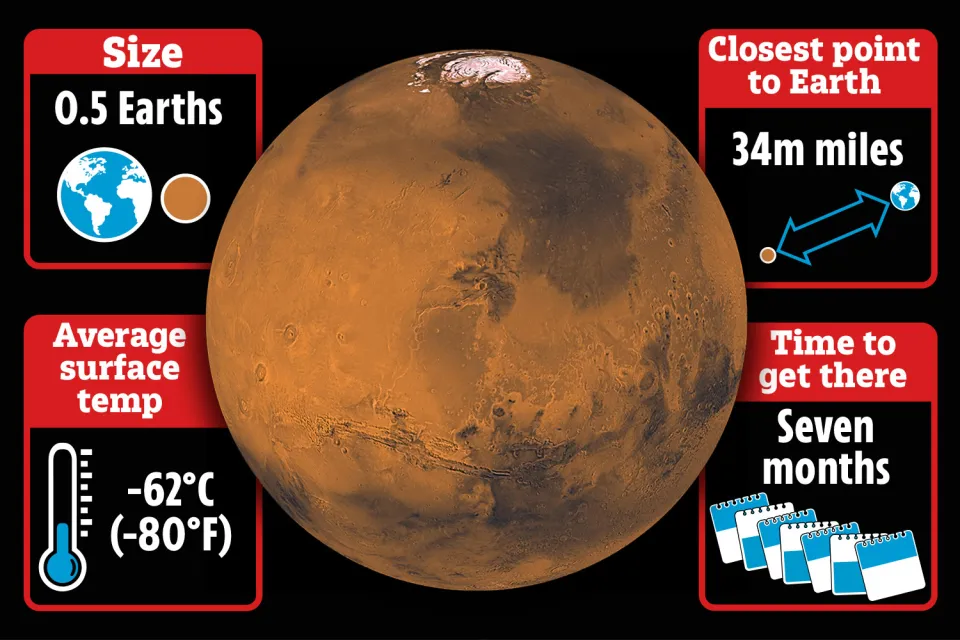
On average, the temperature on Mars is around minus 80 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 60 degrees Celsius). However, this is just a broad estimate, and temperatures fluctuate depending on the time of day, the season, and the location on the planet.Day and Night Temperature Variations
Mars experiences significant temperature swings between day and night due to its thin atmosphere, which lacks the density to retain heat. During the day, temperatures at the equator can rise to about 70 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius). However, once the Sun sets, those same locations can drop to around minus 100 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 73 degrees Celsius) or even lower.Seasonal Differences
Mars has seasons similar to Earth's because its axis is tilted at roughly the same angle as Earth’s (about 25 degrees). However, since Mars takes nearly twice as long to orbit the Sun, its seasons last longer.- During summer, temperatures can peak at around 68 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius) near the equator.
- In winter, temperatures can drop dramatically to minus 195 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 125 degrees Celsius) near the poles.
Temperature by Location
- Equator: Mars' equator experiences the warmest temperatures during the day, which can reach up to 70 degrees Fahrenheit (20 degrees Celsius). But as night falls, temperatures quickly plunge to freezing levels.
- Polar Regions: The poles experience the coldest temperatures. During winter, they can plummet to as low as minus 195 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 125 degrees Celsius).
- Mid-latitudes: These regions are somewhat in-between, with temperatures ranging from minus 20 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 29 degrees Celsius) during the day to minus 90 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 68 degrees Celsius) at night.
Atmospheric Effects on Temperature
Mars’ atmosphere is composed mostly of carbon dioxide (CO₂) but is very thin, only about 1% the density of Earth’s atmosphere. This thin atmosphere is incapable of trapping much heat from the Sun, leading to rapid cooling after sunset and wide temperature variations. Additionally, the lack of moisture in the air further contributes to extreme temperature changes.Dust Storms and Their Influence
Mars is famous for its massive dust storms, which can engulf the entire planet. These storms can have a moderating effect on temperatures by trapping heat in the atmosphere. When a global dust storm occurs, it can raise temperatures across the planet, but the effect is temporary and can obscure the planet’s surface for weeks at a time.Challenges for Human Exploration
The extreme Temperatures on Mars pose significant challenges for human explorers. Equipment, habitats, and suits will need to be designed to withstand both the intense cold and the fluctuations in temperature between day and night. Insulation and heating will be crucial, especially during the frigid Martian nights and winters.Conclusion
Mars is a planet of temperature extremes, ranging from pleasant daytime highs near the equator to deadly cold nights and polar winters. These conditions, shaped by Mars’ thin atmosphere and distance from the Sun, create a harsh environment for future exploration. Understanding these temperatures is essential for planning any human missions or future colonization efforts.Read more :
1= https://bulkdrchecker.com/blogs/what-are-the-temperatures-on-mars/
2= https://bulkdrchecker.com/blogs/what-are-the-tax-brackets/
3= https://bulkdrchecker.com/blogs/what-are-the-tallest-buildings-in-the-world/
4= https://bulkdrchecker.com/blogs/what-are-the-symptoms-of-the-flu/
5= https://bulkdrchecker.com/blogs/what-are-the-symptoms-of-multiple-sclerosis-ms/